Another Big Cyclone Found in Jupiter
Vijayan Sankar (Author) Published Date : Dec 15, 2019 03:44 ISTScience
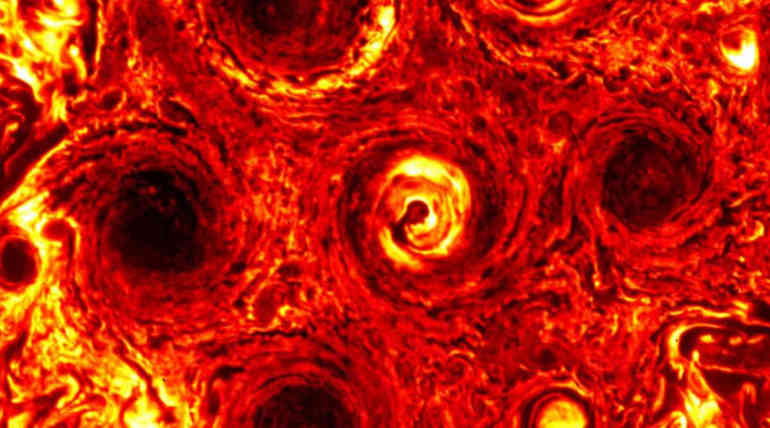
NASA's Juno spots Jovian Cyclone at Jupiter's south pole: NASA's Juno spacecraft, after eight years of its launch, found one more cyclone at the south pole of Jupiter. It was during its 23 science pass, Juno found the storm soaring 2,175 miles above the Jupiter clouds. Data from JIRAM or Jovian Infrared Auroral Mapper suggests that the new cyclone speeds with an average of 225 miles per hour or 362 kilometer per hour and is equal to the size of the Texas city. It is similar to that of its six other cyclones on the south pole found by Juno in 2016, along with nine other storms on the north pole of Jupiter.
Scott Bolton is the Juno spacecraft's principal investigator and is from the Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio. He says that NASA paid again for its combination of creativity and analytical thinking. Juno was lucky enough to escape Jupiter's shadow eclipse, which could freeze it to death. Solar-powered Juno without sunlight could have ended the same way as the Mars Opportunity Rover lost connection due to a dust storm that blocked the sun rays from reaching its solar panels. While jumping the Jupiter's shadow on November 3, Juno has found this new seventh cyclone on the south pole of Jupiter.
Dr. Alessandro Mura is Juno's co-investigator and a researcher with the National Institute for Astrophysics in Rome, Italy. He says that the data from JIRAM indicate that the pentagon arrangement of the six cyclones with one central and five around it is now moved on to hexagonal arrangement. This hexagonal arrangement is massive enough to dwarf the earth, and the new cyclone can engulf Texas state.
NASA's Juno spacecraft started its mission to explore Jupiter on August 5, 2011. Only after five years on July 4, 2016, it reached Jupiter's orbit and found six and nine cyclones on the south and north poles of Jupiter. Now it has found the seventh new cyclone on the south pole. What all it could find more before it ends its journey in July 2021, scientists are eagerly waiting to see.